Telecommunications networks
[Telecommunications networks for two-way voice transmissions (telephone networks)]
[Telecommunications networks for data transmission]
[ Fusion of voice and data transmission via Voice over IP technology]
Telecommunications networks are transmission equipment that can transmit information with electromagnetic or optical signals between different locations, analog or digital. The report can be audio, video, or other data. Networks remain based on wired or wireless infrastructures. Typical telecommunications networks are the fixed telephone network, the mobile telephone network, cable television networks or the Internet.
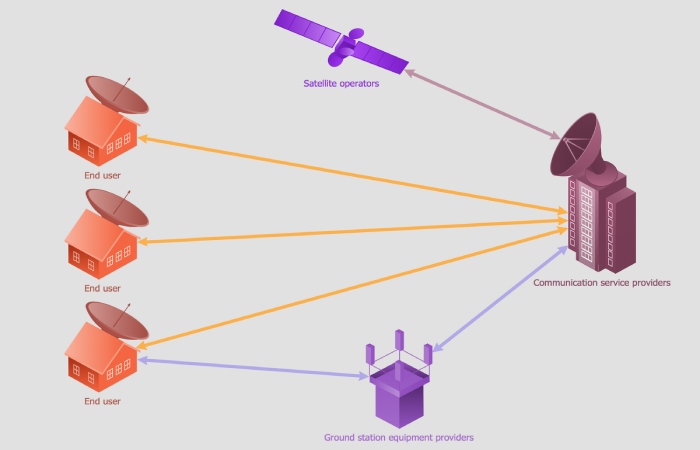
Table of Contents
Telecommunications Networks for two-way Voice Transmissions (telephone networks)
Different type of telephone networks can still remain used for two-way voice transmission. In the early days of telephony, the telephone network was performance-based and transferred voice signals using electromagnetic analog signals. Today, telephone networks are digital and can be built with cables (landline) or wireless (mobile network). Connection establishment between participants has shifted from strictly circuit switched operation to packet switched systems.
Telecommunications Networks for Data Transmission
In the past, telecommunications networks for transmitting data used many different protocols. Following the success of the Internet, the Internet Protocol (IP) has increasingly established itself as the standard protocol for data transmission. Today almost all data networks operate over IP.
Data remain shared on these networks by individual data packets that carry the destination and source addresses. At the nodes on the web, destination addresses stay evaluated by so-called routers and data packets remain sent to the next node in the direction of the destination.But, In principle, individual packages can take different paths through the network and arrive at their destination at other times. The target system puts them back in the correct order.
Fusion of voice and data transmission using voice over IP technology
The increased presentation of IP networks, short latency times, low jitter values and high bandwidth make data networks suitable for critical real-time applications such as telephony. Likewise, telephone networks, thanks to Voice over IP technology, remain almost completely merged with data networks. But, It has the advantage that the operator only has to operate a single infrastructure to transmit voice and data.
Similarly, A number of new applications remain provided to the user which provides flexibility
communication possibilities. Also, In this way, phone systems be able to operate entirely cloud-based. But, Users no longer need to have their system software and can use all telephony services anywhere with Internet access.
What is a Data Transmission Network?
The data transmission network remain called the set formed by the equipment and the physical and logical means that allow the communication of information between different users at any distance. These networks can be local (LAN) or global (WAN).
What are the Data Transmission Measures?
Transmission time remains measured from the moment the first bit is put on the line to the last bit of the packet to stay transmitted. The unit of size in the International System (if contemplated in it) would be in bits/second (b / s or also bps) or expressed in octets or bytes (B / s).
Related searches
[4 types of telecommunication networks]
[telecommunications network examples]
[telecommunication network architecture]
[telecommunication and networking pdf]
[basics of telecommunication networks]
[telecommunication network model]
[networking and telecommunications technology examples]
[telecommunication network ppt]

